Comparing Organic and Conventional Farming: Which is Better for Indonesia?
Understanding Organic and Conventional Farming
Indonesia, with its vast and fertile landscapes, is a significant player in the agricultural sector. Two prominent farming methods, organic and conventional, are often compared to determine which is more beneficial for the nation. Each method has its unique advantages and challenges, contributing differently to the economy, environment, and health.
Organic farming relies on natural processes and materials to grow crops. It emphasizes biodiversity, ecological balance, and soil health. Conventional farming, on the other hand, uses chemical fertilizers and pesticides to maximize crop yields and efficiency. Understanding both methods' intricacies helps in evaluating their impacts effectively.
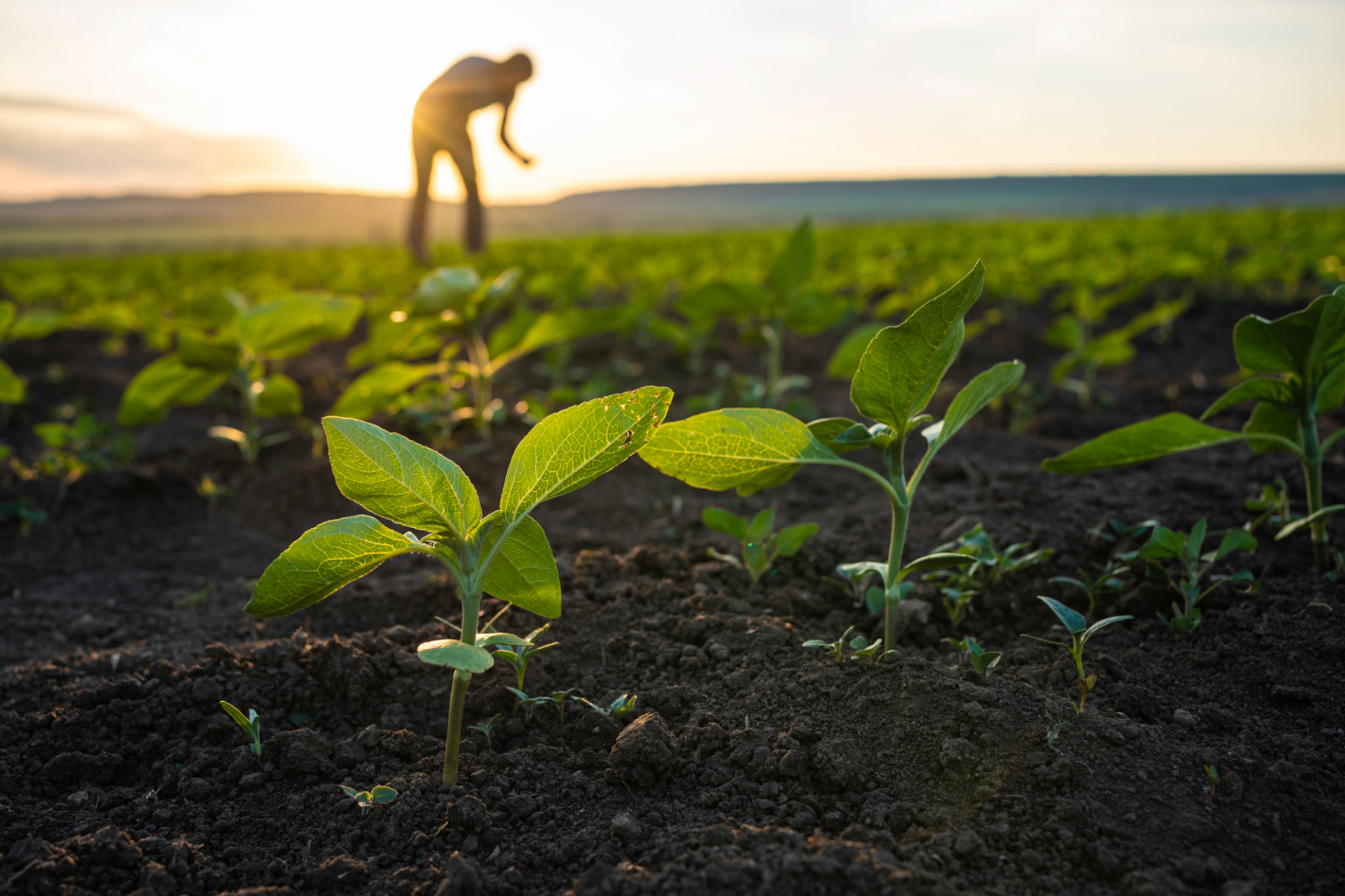

Environmental Impact: A Crucial Consideration
One of the primary concerns with conventional farming is its environmental impact. The use of synthetic chemicals can lead to soil degradation, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity. These issues are particularly concerning in Indonesia, where maintaining rich biodiversity is critical for the ecosystem's stability.
Organic farming tends to have a lesser environmental footprint. By avoiding synthetic chemicals, it promotes healthier soils and cleaner waterways. Additionally, organic practices support biodiversity by fostering habitats for various species. However, organic farming often requires more land to produce the same yield as conventional methods, which could lead to deforestation if not managed sustainably.

Economic Factors: Weighing Costs and Benefits
The economic aspect of farming is an essential factor for Indonesia's agricultural sector. Conventional farming is often seen as more cost-effective due to higher yields and lower labor costs. The use of machinery and chemical inputs allows for large-scale production, making it appealing for commercial farmers.
Conversely, organic farming can be more labor-intensive and often yields less than conventional methods. However, the growing global demand for organic products can lead to premium pricing, offering potential for higher profits. For small-scale farmers in Indonesia, organic farming could present an opportunity to tap into niche markets while promoting sustainable practices.
Health Implications: Ensuring Food Safety
Food safety and health are paramount when comparing these farming methods. Conventional farming's reliance on chemical pesticides raises concerns about residue in produce, which can affect consumer health if not properly managed. This issue is crucial for Indonesia as it strives to improve its food safety standards.
Organic farming typically offers produce with lower pesticide residues, aligning with growing consumer preferences for natural and health-conscious food options. This attribute can enhance public health and build consumer trust in local produce. Nevertheless, organic products must still be carefully managed to prevent contamination and spoilage.
Conclusion: Finding Balance for Indonesia's Future
Determining which farming method is better for Indonesia involves balancing multiple factors including environmental sustainability, economic viability, and health benefits. Each method presents unique opportunities and challenges that need to be considered within the local context.
Ultimately, a hybrid approach that integrates the best practices of both organic and conventional farming could provide a sustainable solution. By adopting innovative techniques and policies that promote sustainable agriculture, Indonesia can enhance its food security, protect its environment, and boost its economy.
